The Backbone of Road Rehabilitation: Tungsten Carbide Road Milling Tools
Industry News-The infrastructure of modern civilization relies heavily on well-maintained road networks. A critical process in this maintenance cycle is road milling (also known as cold planing or profiling), which involves the removal of the top layer of existing pavement to prepare a uniform surface for new asphalt or concrete application. Central to the efficiency and cost-effectiveness of this operation are Tungsten Carbide Road Milling Tools.
The Unrivaled Material: Tungsten Carbide
Tungsten carbide ($\text{WC}$) is a composite material, often referred to as a “cemented carbide,” comprising fine particles of tungsten carbide bonded together by a metallic binder, most commonly cobalt ($\text{Co}$). This unique combination results in a material that boasts exceptional properties, making it an ideal choice for the extreme demands of pavement removal.
- Extreme Hardness: Tungsten carbide’s hardness, second only to diamond, allows it to effectively cut through the abrasive matrix of asphalt and aggregate stones without quickly dulling.
- Superior Wear Resistance: The material resists the constant, high-speed abrasion encountered during milling, significantly extending tool life compared to traditional steel tools.
- High Compressive Strength: It can withstand the immense forces and impact loads generated when a rotating milling drum engages with hardened pavement.
- Heat Stability: It maintains its critical cutting-edge hardness even as high friction generates considerable heat.
Anatomy of the Milling Tool
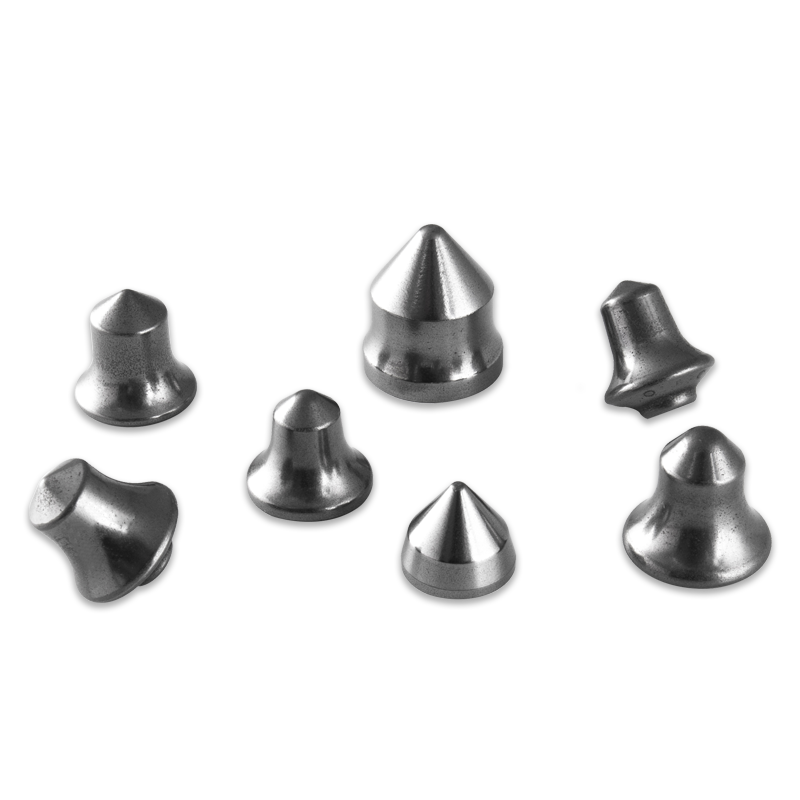
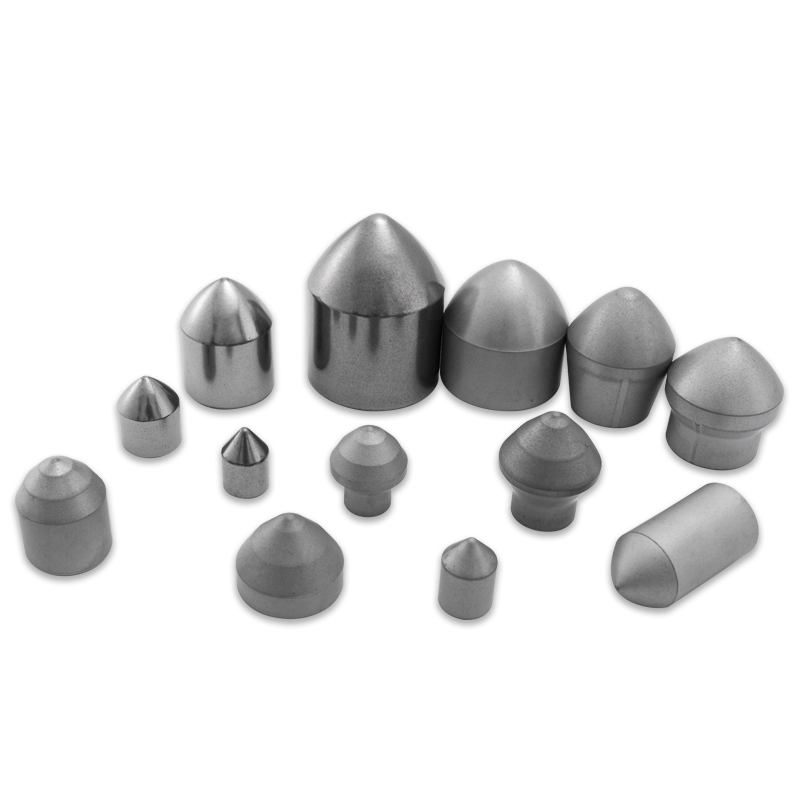
The primary tool used in the milling process is a conical cutting bit or pick. While the specific design varies by manufacturer and application (e.g., asphalt vs. concrete), all effective Tungsten Carbide Road Milling Tools share a core structure engineered for performance:
- The Carbide Tip: This is the working head of the tool, typically sintered tungsten carbide. Its grade (determined by $\text{WC}$ grain size and cobalt content) is selected based on the material being milled—finer grains and lower cobalt for harder materials like concrete, and coarser grains and higher cobalt for toughness in asphalt.
- The Steel Shank/Body: This robust body connects the carbide tip to the tool holder on the milling drum. It must be strong and tough to absorb impact and flexing forces without breaking.
- The Retaining System: A groove or collar design that allows for the tool to rotate in the holder for self-sharpening wear and enables quick-change functionality for rapid replacement when a bit is worn or damaged.
Operational Benefits in Road Rehabilitation
The adoption of Tungsten Carbide Road Milling Tools has fundamentally improved the road rehabilitation industry, translating directly into tangible economic and operational benefits:
| Benefit | Description | Impact on Projects |
|---|---|---|
| Increased Productivity | Tools maintain their sharp cutting edge for longer, allowing machines to operate at consistent speeds and higher removal rates. | Faster project completion and reduced machine operating hours. |
| Reduced Downtime | Fewer tool changes are required throughout the workday due to superior wear life. Quick-change systems further minimize the time needed for maintenance. | Maximized on-site work time and lower labor costs for tool servicing. |
| Lower Cost-Per-Square-Yard | While the initial cost of a tungsten carbide tool is higher than steel, its dramatically extended lifespan and improved efficiency lead to a lower total cost over the life of the project. | Improved project profitability and optimized budget allocation. |
| Consistent Surface Quality | The sustained cutting performance ensures a uniform milled surface (profile) that is crucial for the bonding and longevity of the new pavement layer. | Higher quality final road surface and less need for rework. |
Advancements and Future Outlook
The industry continues to innovate, focusing on optimizing the microstructure of the tungsten carbide material itself. Modern advancements include:
- Nano-Technology Carbide: Enhancements to the cobalt binder matrix to optimize toughness and wear resistance at the nanoscale, leading to even more flexible and durable bits.
- Improved Brazing Techniques: Better methods for bonding the carbide tip to the steel shank to prevent premature failure due to impact and thermal stress.
- Specialized Geometries: Development of unique tip shapes and sizes to address specific challenges, such as heavily-grooved pavements or ultra-hard concrete.
As road networks age and the demand for efficient, high-quality pavement maintenance increases, Tungsten Carbide Road Milling Tools will remain an indispensable technology, driving productivity and sustainability in the global construction and infrastructure sector.


 English
English русский
русский