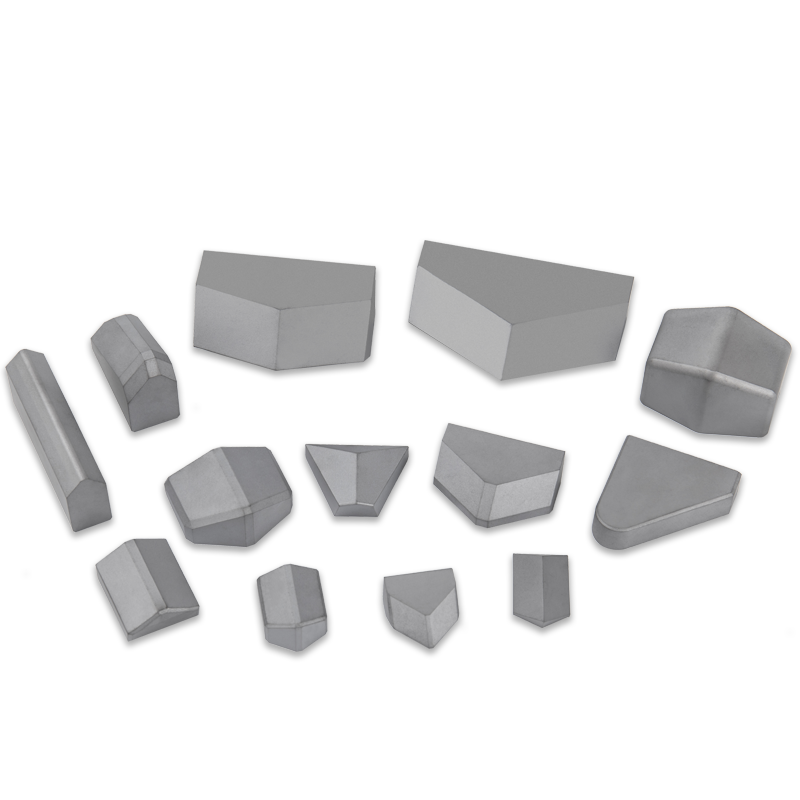
Tungsten Carbide Stamping Dies: The Cornerstone of Precision Manufacturing
Industry News-In modern manufacturing, stamping is an efficient and economical metal-forming process widely used in various fields like automotive, electronics, and home appliances. The precision and quality of stamped parts largely depend on the molds used. Among these, Tungsten Carbide Stamping Dies have become the preferred choice for high-precision, long-life molds due to their exceptional performance.
What is Tungsten Carbide?
Tungsten Carbide, or WC-Co alloy, is a composite material created through powder metallurgy. It consists of Tungsten Carbide micro-particles as the hard phase, bonded together by cobalt (Co). What makes this material unique is that it combines the high hardness of ceramics with the high toughness of metals.
The hardness of Tungsten Carbide is extremely high, second only to diamond. This allows Tungsten Carbide Stamping Dies to withstand immense pressure and wear during the stamping process. The cobalt binder, on the other hand, provides the necessary toughness, making the material resistant to fractures and extending the mold's service life.
Advantages of Tungsten Carbide Stamping Dies
Compared to traditional tool steel, Tungsten Carbide Stamping Dies offer several significant advantages:
-
Extreme Wear Resistance: Tungsten Carbide is several times harder than tool steel. Its superior wear resistance is particularly evident in high-intensity stamping operations, especially when working with hard materials like stainless steel and silicon steel sheets. This significantly extends the mold's service life, reduces the frequency of replacement and maintenance, and ultimately lowers production costs.
-
Exceptional Compressive Strength and Rigidity: Tungsten Carbide boasts extremely high compressive strength, allowing it to withstand the immense impact forces generated during stamping. Its high rigidity also ensures the mold's geometric accuracy during operation, reducing deformation and guaranteeing the consistency of stamped parts.
-
Superior Surface Finish: Due to the material's density and hardness, the mold cavity can be precisely ground and polished to an extremely high surface finish. This not only aids in the smooth ejection of stamped parts but also improves the surface quality of the parts and reduces burrs.
-
High Precision: In industries requiring extreme precision, such as microelectronics and precision connectors, Tungsten Carbide Stamping Dies can be manufactured with very tight tolerances using high-precision wire cutting, electrical discharge machining (EDM), and grinding processes. This ensures the final product meets stringent accuracy requirements.
Thanks to their outstanding performance, Tungsten Carbide Stamping Dies are widely used in demanding industries, including:
-
Electronics: For stamping small, high-precision electronic components like precision connectors, lead frames, and chip encapsulation supports.
-
Automotive: For stamping high-strength steel plates and laminating motor stators and rotor cores.
-
Medical Devices: For manufacturing precision medical components like surgical blades and needle tubes.
-
Home Appliances: For producing key components like compressor valve plates and motor cores.
Key Technologies in Manufacturing Tungsten Carbide Molds
Manufacturing a high-quality Tungsten Carbide Stamping Die is a complex and precise engineering process involving several key technologies:
-
Material Selection: The appropriate grade of Tungsten Carbide is chosen based on factors such as the material being stamped, stamping thickness, and pressing force. Different grades offer varying levels of hardness, toughness, and wear resistance to meet specific working conditions.
-
Precision Machining: The extreme hardness of Tungsten Carbide makes traditional cutting difficult. Mold shaping primarily relies on specialized techniques:
-
Wire EDM (Electrical Discharge Machining): Used to cut complex contours, especially for creating punches and dies.
-
Die Sinking EDM: Used to machine mold cavities, blind holes, and other intricate shapes.
-
Precision Grinding: Using specialized grinding machines, the surfaces of Tungsten Carbide molds can be ground to achieve the required dimensional accuracy and surface finish.
-
-
Mold Design: The design of a Tungsten Carbide mold must fully account for the material's characteristics. Since its toughness is lower than that of tool steel, the design should avoid sharp corners and thin walls that could lead to stress concentration. Modular design is often used to facilitate easy replacement and maintenance of parts.
Conclusion
Tungsten Carbide Stamping Dies have become an indispensable tool in modern precision stamping manufacturing due to their unparalleled wear resistance, high strength, and precision. They not only guarantee high-quality and high-efficiency production but also represent a key technology that drives the manufacturing industry to a higher level. As demands for product precision and production efficiency continue to rise, the application of Tungsten Carbide Stamping Dies will become even more widespread, and the technology will continue to innovate.


 English
English русский
русский