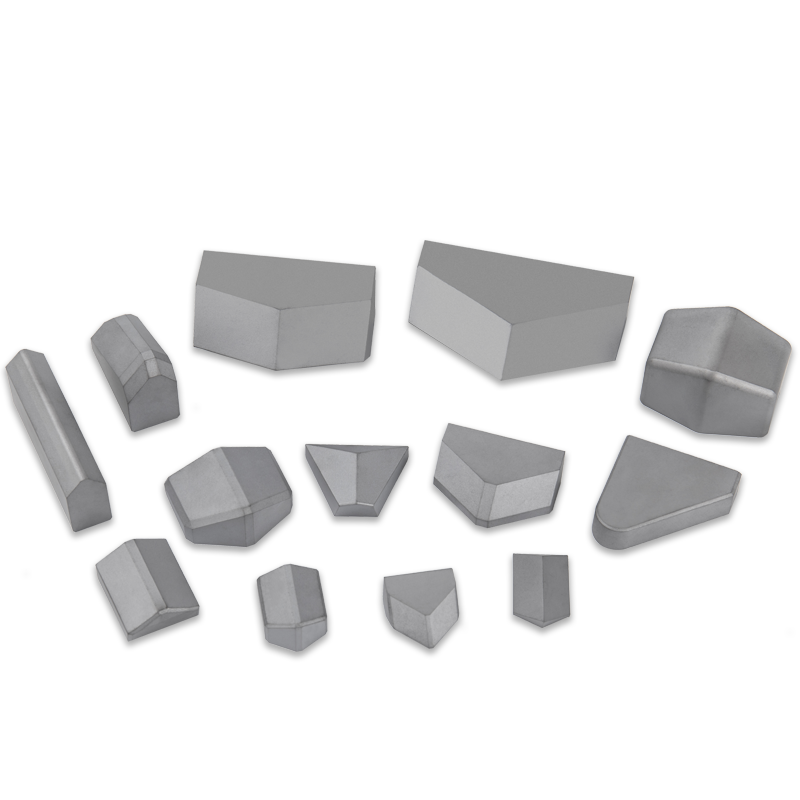
The Unstoppable Edge: Exploring Tungsten Carbide Cutting Blades
Industry News-The King of Hardness
The world of manufacturing, construction, and specialized craftsmanship relies on materials that can stand up to the most demanding tasks. When it comes to cutting, drilling, and shaping incredibly hard substances, one material reigns supreme: tungsten carbide.
What Makes Tungsten Carbide So Special?
Tungsten carbide () is a chemical compound containing equal parts tungsten and carbon atoms. What gives it its legendary status?
- Exceptional Hardness: Tungsten carbide’s hardness is its most famous trait, typically registering between 8.5 and 9.0 on the Mohs scale, second only to diamond. This extreme hardness allows it to slice through materials like steel, hardwoods, and even ceramics that would quickly dull a conventional steel blade.
- High Strength and Rigidity: It resists deformation and maintains its sharp edge even under immense pressure and high temperatures, which are common during high-speed cutting operations.
- Abrasion Resistance: Its structure makes it highly resistant to wear and tear caused by friction, significantly extending the life of the tool.
The Workhorse: Tungsten Carbide Cutting Blade
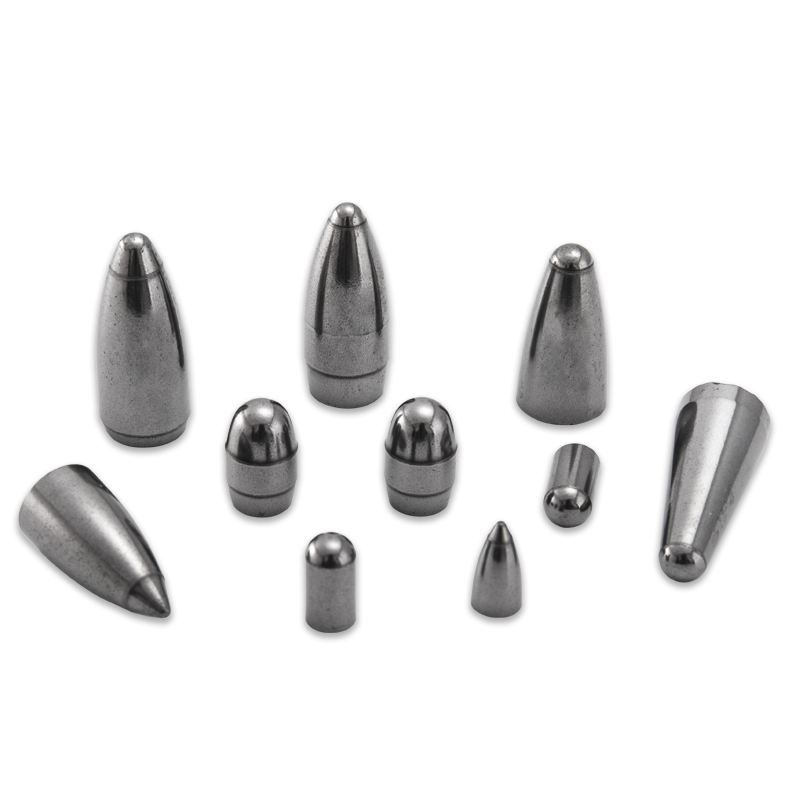
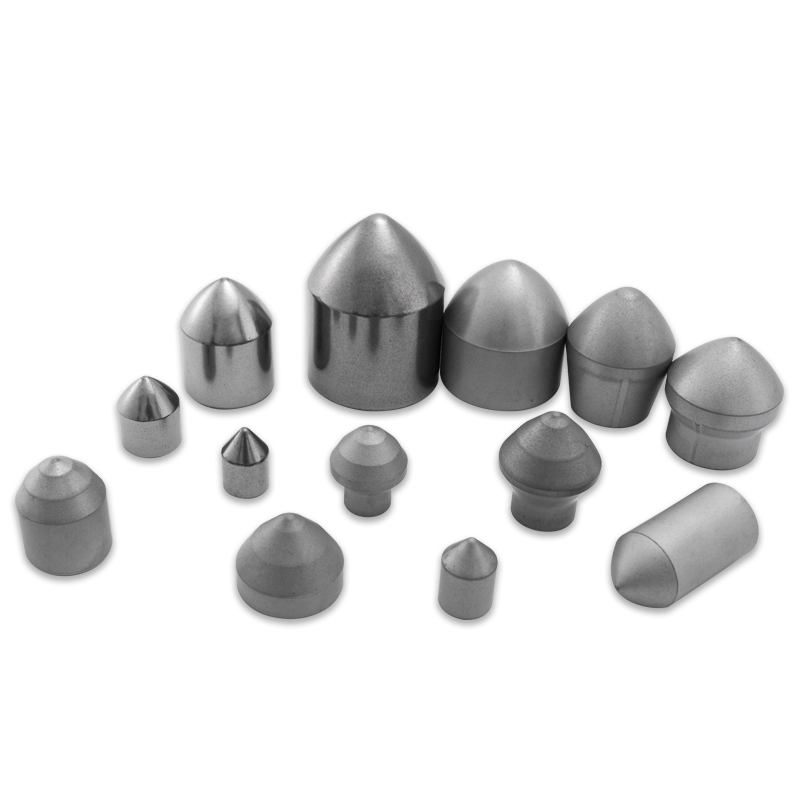
A Tungsten Carbide Cutting Blade is an essential component in various industrial and commercial applications, from saw blades to drill bits and specialized machine tooling. These blades aren’t typically made of pure tungsten carbide, but rather a composite material created through a process called sintering.
From Powder to Precision Tool
The process of creating a tungsten carbide cutting tool involves a few critical steps:
- Powder Mixing: Fine tungsten carbide powder is mixed with a binder metal, most commonly cobalt. The cobalt acts like a glue, holding the hard tungsten carbide grains together.
- Compaction: The mixed powder is pressed into the desired shape of the blade or insert.
- Sintering: The compacted shape is heated to a temperature below the melting point of tungsten carbide, but high enough for the cobalt binder to liquefy. As the cobalt cools and solidifies, it creates a tough, composite material often referred to as a cemented carbide or hardmetal. The final product has the extreme hardness of tungsten carbide, coupled with the necessary toughness provided by the cobalt.
Applications Across Industries
The durability and performance of the Tungsten Carbide Cutting Blade make it indispensable across a range of fields:
- Woodworking: Carbide-tipped saw blades can cut dense hardwoods and composite materials with far greater speed and longevity than high-speed steel blades. Router bits tipped with carbide are the standard for precision shaping.
- Metalworking: In lathes, milling machines, and other machining centers, small, replaceable tungsten carbide inserts are used to cut and shape steel and other metals at incredibly high speeds and temperatures.
- Construction and Mining: Drill bits used for boring through rock, concrete, and asphalt often feature robust tungsten carbide tips to withstand the abrasive environment.
- Medical and Aerospace: Due to its precision and hardness, tungsten carbide is also used in specialized surgical instruments and components for aerospace manufacturing where extreme material requirements are necessary.
The Future of Cutting Technology
As industries continue to demand faster production speeds and the ability to process new, harder composite materials, the role of the Tungsten Carbide Cutting Blade will only grow more critical. Ongoing research focuses on developing new coatings and advanced binder materials to further enhance the heat resistance and performance of these already phenomenal tools, ensuring that the king of hardness remains on the cutting edge of technology.


 English
English русский
русский