Unlocking Efficiency with TBM Tungsten Carbide Inserts
Industry News-In the realm of modern tunnel construction, Tunnel Boring Machines (TBMs) play a pivotal role in ensuring efficient and precise excavation through various geological conditions. At the heart of this performance lie the TBM Tungsten Carbide Inserts, engineered to withstand extreme pressure and abrasion. These specialized cutting components have revolutionized the tunneling industry by enhancing the durability and productivity of TBM cutter heads.
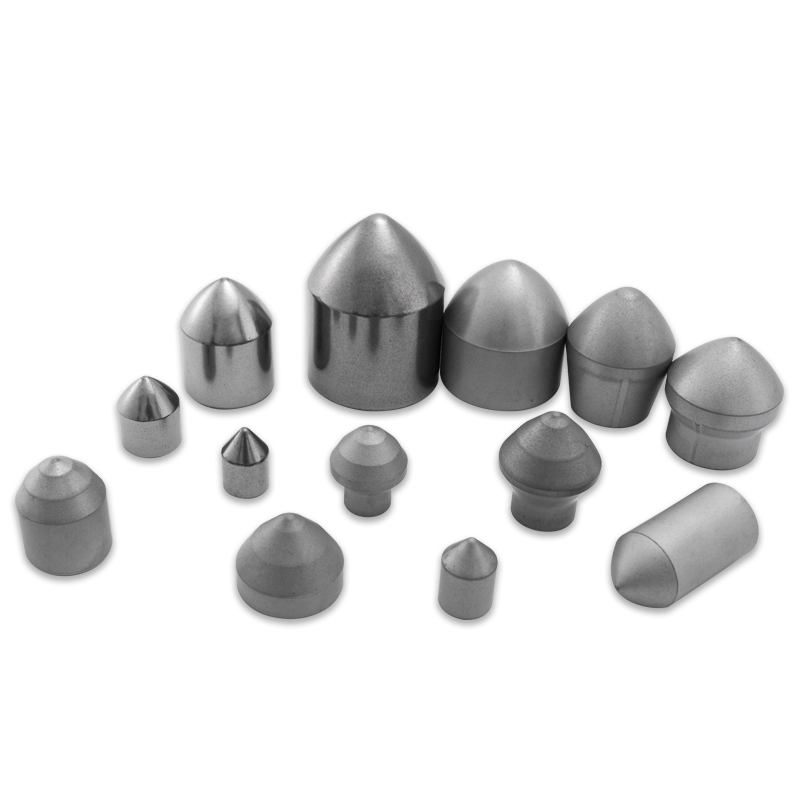
Tungsten Carbide Inserts for TBMs are hard, wear-resistant components affixed to the cutting tools of tunnel boring machines. Made from a compound of tungsten and carbon, these carbide cutting inserts boast exceptional hardness and thermal resistance. Their primary role is to break and displace rock, soil, and other underground materials during the excavation process.
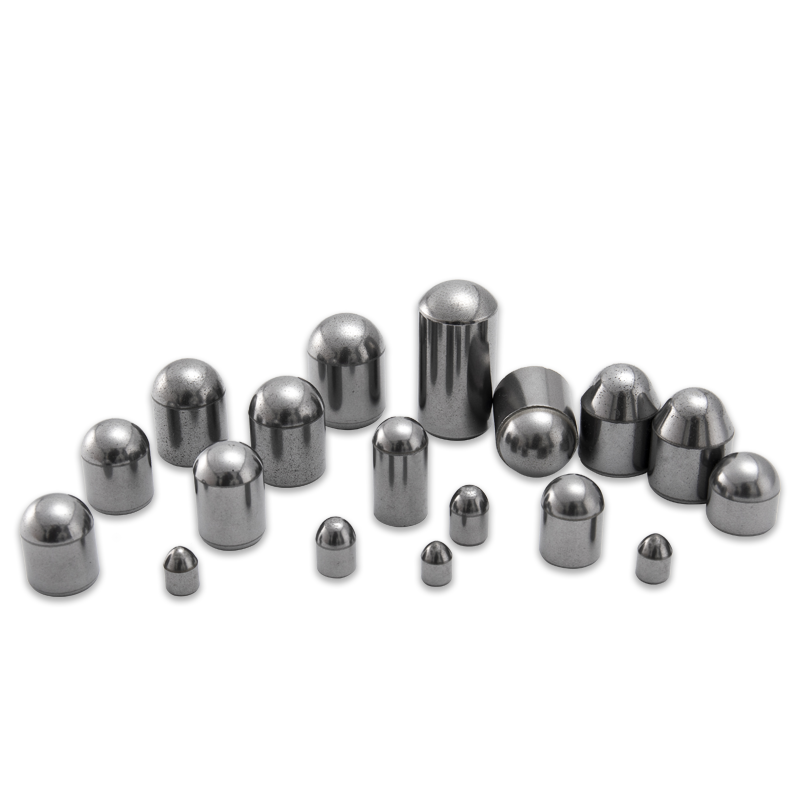
Often referred to as TBM cutter bits, these inserts are vital in reducing wear on the machine's cutter head, thereby extending the lifespan of the equipment and minimizing downtime. Depending on the type of TBM—earth pressure balance (EPB), slurry, or hard rock—the shape, size, and grade of the tungsten carbide insert can vary.
Advantages of Tungsten Carbide Inserts in TBMs
One of the key reasons for the popularity of tungsten carbide TBM inserts is their exceptional wear resistance. As TBMs operate under high loads and abrasive conditions, conventional steel tips would wear down rapidly. Tungsten carbide, however, offers superior durability, ensuring that the machine can operate longer without frequent tool changes.
Additionally, these carbide inserts exhibit excellent toughness and thermal conductivity, essential in maintaining cutting efficiency even under high friction. As a result, TBM operators experience lower maintenance costs, improved penetration rates, and higher overall productivity.
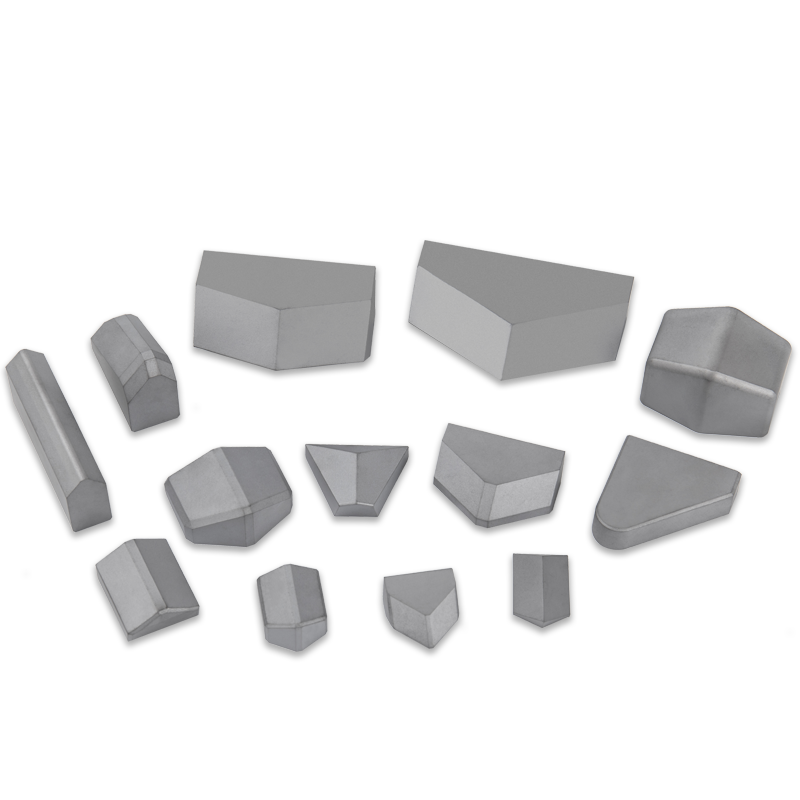
Applications and Suitability
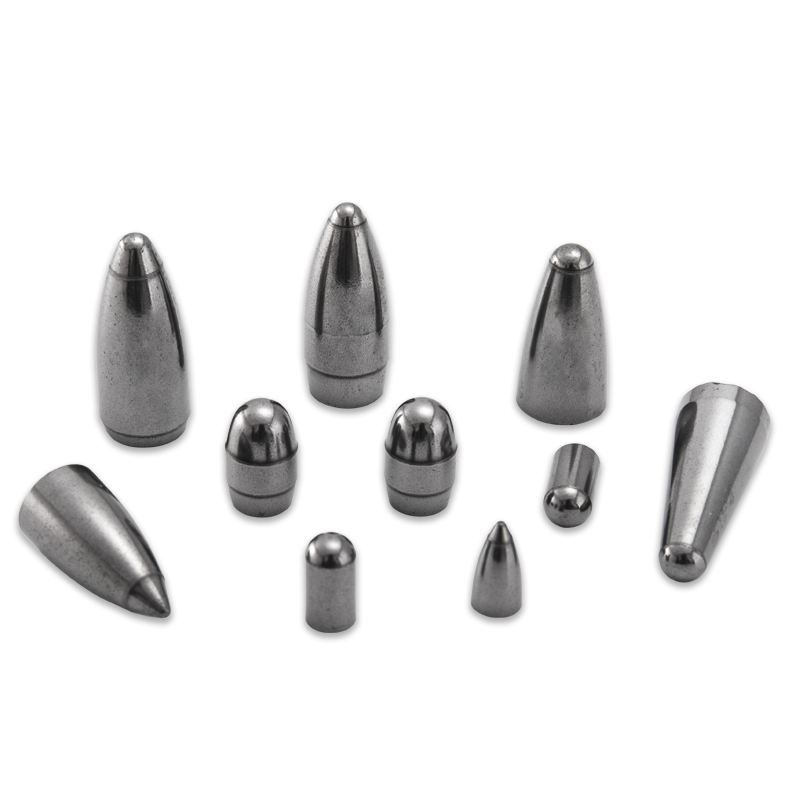
TBM tungsten carbide tools are used in a wide range of tunneling projects, from subway construction and hydroelectric tunnels to sewer lines and mining applications. Their ability to handle varied rock formations—including granite, basalt, shale, and limestone—makes them a versatile solution across multiple industries.
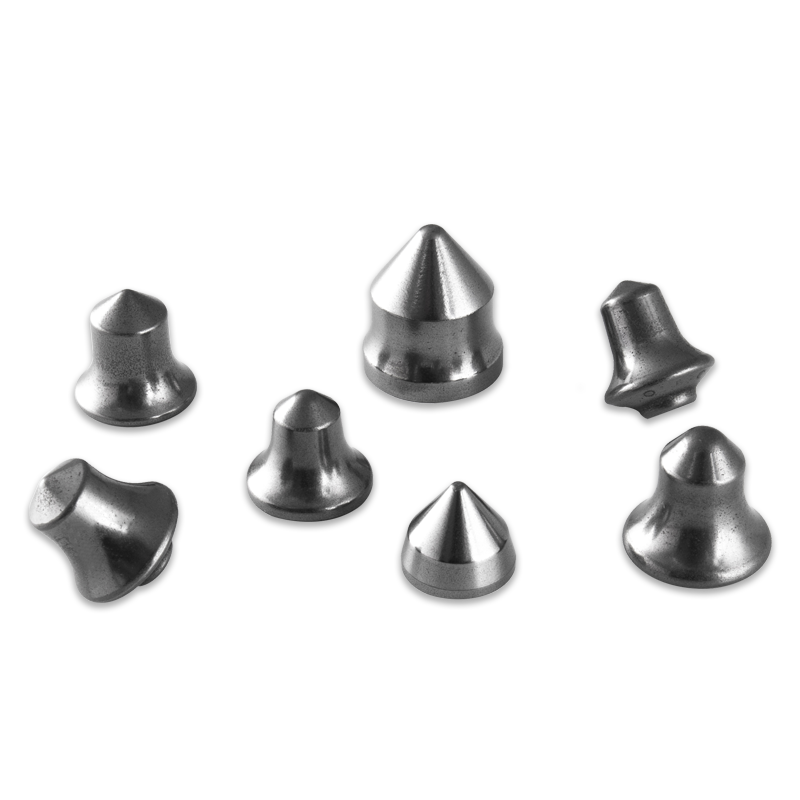
Moreover, manufacturers tailor TBM cutting inserts to suit specific geological challenges. For instance, inserts designed for hard rock tunneling feature thicker, reinforced tips, while those for softer soils may have a sharper geometry for better penetration.
Material Composition and Manufacturing
The success of TBM tungsten carbide cutting tools lies in their material composition. Typically, these inserts are manufactured using a powder metallurgy process, combining tungsten powder with a binder such as cobalt. The resulting compound is then sintered at high temperatures to achieve maximum hardness and density.
To further improve performance, some TBM cutter inserts undergo surface treatments such as coating or fine grinding. These processes enhance resistance to chipping and improve cutting accuracy.
Choosing the Right Tungsten Carbide Inserts
Selecting the appropriate TBM carbide inserts involves evaluating several factors, including rock hardness, machine type, and cutting head design. Collaboration with experienced suppliers and manufacturers ensures that the inserts are engineered for optimal performance in specific project conditions.
When choosing a carbide cutting insert for TBM, considerations should include:
Grade and composition of the carbide
Insert shape and tip geometry
Wear resistance and impact strength
Compatibility with cutter head layout


 English
English русский
русский